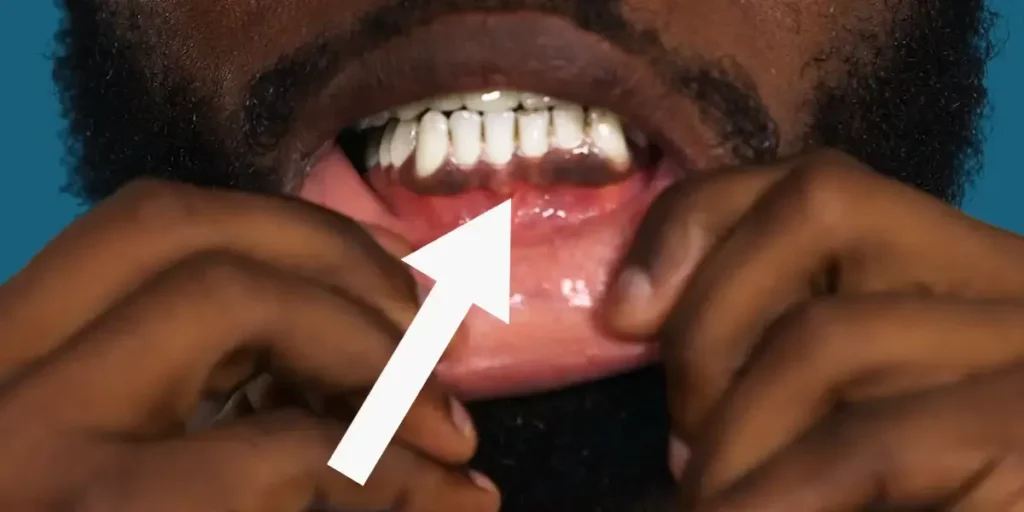
Black gums can be a cause for concern, especially if they are accompanied by other symptoms such as pain, swelling, or bleeding.
If you’ve noticed that your gums are darker than usual, it’s important to seek professional dental care to determine the underlying cause and explore treatment options.
Causes of Black Gums
There are several possible causes of black gums, including genetics, smoking, certain medications, and poor oral hygiene.
Some people may simply have naturally darker gums, while others may develop black gums over time due to external factors.
Smoking, for example, can cause the gums to darken due to the chemicals in tobacco products.
Certain medications, such as minocycline or antimalarials, can also cause gum pigmentation.
Poor oral hygiene habits can lead to gum disease, which can cause the gums to appear darker or even black.
Problems that can occur as a result of black gums
Black gums can be a sign of several different conditions or factors, and the problems that can occur as a result of black gums can vary depending on the underlying cause. Here are some potential issues:
- Poor oral hygiene: Black gums can be caused by a buildup of plaque and bacteria on the teeth and gums. This can lead to gum disease, which can cause gum recession, tooth loss, and even systemic health problems if left untreated.
- Smoking: Smoking can cause black gums, as well as a host of other oral health problems, including gum disease, tooth loss, and oral cancer.
- Medications: Certain medications can cause black gums as a side effect. This is particularly true of medications that contain iron, such as some types of blood thinners and supplements.
- Melanin hyperpigmentation: Some people naturally have more melanin in their gums, which can cause them to appear darker in color. This is generally not a problem and does not require treatment.
- Other medical conditions: In rare cases, black gums can be a symptom of certain medical conditions, such as Addison’s disease, Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, or systemic sclerosis.
If you are experiencing black gums, it’s important to see a dentist or periodontist for an evaluation to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
Diagnosis of Black Gums
If you’re concerned about the color of your gums, it’s important to schedule an appointment with a dental professional.
During a diagnosis appointment, the dentist will perform a visual examination of your gums and may also take a biopsy if necessary.
This can help determine the underlying cause of your black gums and guide treatment options.
What’s the first step to curing black gums
The first step to curing black gums/ gum discoloration is to determine the underlying cause of the discoloration.
This will help guide the appropriate treatment approach.
If the discoloration is due to poor oral hygiene or smoking, the first step would be to improve oral hygiene habits and quit smoking.
This may involve brushing and flossing regularly, using mouthwash, and seeing a dentist or periodontist for a professional cleaning.
If the discoloration is due to medication or a medical condition, a person should speak with their healthcare provider to discuss alternative medication options or medical treatments.
If the discoloration is due to melanin hyperpigmentation, it may not require any treatment at all.
However, if a person is bothered by the appearance of their gums, they can discuss treatment options with a dentist or periodontist, such as gum depigmentation.
In any case, it’s important to see a dental professional for an evaluation and diagnosis before attempting any treatments for black gums.
Treatment Options for Black Gums
Depending on the underlying cause of your black gums, there are several possible treatment options:
- Scaling and root planning: This is a deep cleaning procedure that can remove plaque and tartar buildup from the gum line, helping to reduce pigmentation and prevent further damage.
- Laser treatment: Laser treatment uses a specialized laser to remove pigmentation from the gums, providing a less invasive alternative to traditional surgery.
- Gum grafting: This is a surgical procedure that can replace damaged gum tissue with healthy tissue from another part of the mouth, helping to restore the appearance and function of the gums.
- Medications: Certain prescription medications can help reduce gum pigmentation, although these are typically only used in severe cases.
Home remedies to curing and avoiding black gums
While home remedies may help improve the appearance of black gums or prevent them from occurring, it’s important to note that the effectiveness of these remedies may vary depending on the underlying cause.
Here are some potential home remedies to consider:
- Oil pulling: This involves swishing a tablespoon of oil (such as coconut or sesame oil) around in your mouth for 15-20 minutes and then spitting it out. Some people believe this can help remove bacteria and toxins from the mouth, which may improve gum health.
- Saltwater rinse: Gargling with a mixture of warm water and salt may help reduce inflammation and kill bacteria in the mouth, which can improve gum health.
- Baking soda: Brushing with a paste made of baking soda and water may help remove surface stains and plaque buildup from the teeth and gums.
- Vitamin C: Eating foods high in vitamin C, such as citrus fruits and leafy greens, may help improve gum health by boosting collagen production and reducing inflammation.
- Avoiding smoking: If you smoke, quitting smoking is one of the most important steps you can take to prevent black gums and improve overall oral health.
However, it’s important to note that these remedies should not replace regular dental care or treatment prescribed by a healthcare professional.
If you are experiencing black gums, it’s important to see a dentist or periodontist for an evaluation and diagnosis to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
Gum bleaching
Gum bleaching, also known as gum depigmentation, is a cosmetic dental procedure that involves removing excess pigmentation from the gums to improve their appearance.
This is typically done using a special laser or a surgical scalpel to remove the top layer of tissue, revealing lighter, pinker gum tissue beneath.
Gum bleaching may be recommended for individuals who have naturally dark gums due to genetics or ethnic background, or for those who have experienced discoloration due to certain medications, smoking, or other factors. It is typically a safe and effective procedure that can be performed in a dental office.
However, as with any medical procedure, there are risks associated with gum bleaching.
These may include infection, bleeding, swelling, and sensitivity in the treated area. It’s important to discuss these risks with your dentist or periodontist before undergoing the procedure.
Additionally, gum bleaching may not be appropriate for everyone.
Individuals with certain medical conditions or who are taking certain medications may not be good candidates for the procedure.
Your dentist or periodontist can help determine if gum bleaching is right for you and recommend alternative treatment options if necessary.
It’s also important to note that while gum bleaching can improve the appearance of dark or discolored gums, it does not address underlying gum disease or other oral health issues.
Regular dental care, including brushing, flossing, and professional cleanings, is essential for maintaining healthy gums and preventing further damage or discoloration.
Prevention of Black Gums
To prevent black gums from developing in the first place, it’s important to maintain good oral hygiene habits.
This includes brushing your teeth twice a day, flossing regularly, and visiting the dentist for regular checkups and cleanings.
If you smoke, quitting can also help reduce your risk of developing black gums.
Additionally, avoiding certain foods and drinks that can stain the teeth and gums, such as coffee, tea, and red wine, can help keep your gums looking healthy.
Take away
Black gums can be a cause for concern, but with proper diagnosis and treatment, they can be effectively managed.
If you’re concerned about the color of your gums, be sure to schedule an appointment with a dental professional to determine the underlying cause and explore treatment options.
By maintaining good oral hygiene habits and taking steps to prevent gum disease, you can help keep your gums looking healthy and vibrant.