Gum disease is one of the most common — and most underestimated — oral health conditions.
Many people don’t realise they have it until it has progressed to a more advanced stage.
At Every Smile Dental, we believe early detection and prevention are your best defence.
Here’s what causes gum disease, the symptoms to look out for, and the treatments that can restore your gum health.
Quick Summary: Gum Disease Essentials
- Caused primarily by plaque and tartar build-up
- Early stage (gingivitis) is reversible with treatment
- Advanced stage (periodontitis) can cause bone loss and tooth loss
- Warning signs: bleeding gums, bad breath, gum recession, loose teeth
- Preventable with consistent home care and professional cleanings
What Is Gum Disease?
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is an infection of the tissues that support your teeth.
It typically starts with gingivitis—a mild, reversible form of gum inflammation—and can progress to periodontitis, a more serious condition that can lead to tooth loss if left untreated.
What Causes Gum Disease?
The primary cause of gum disease is plaque—a sticky film of bacteria that forms on your teeth.
If plaque is not removed through regular brushing and flossing, it hardens into tartar, which can only be removed by a dental professional.
Other contributing factors include:
- Poor oral hygiene
- Smoking or tobacco use
- Hormonal changes (such as during pregnancy)
- Diabetes
- Certain medications that reduce saliva flow
- Genetics or a family history of gum disease
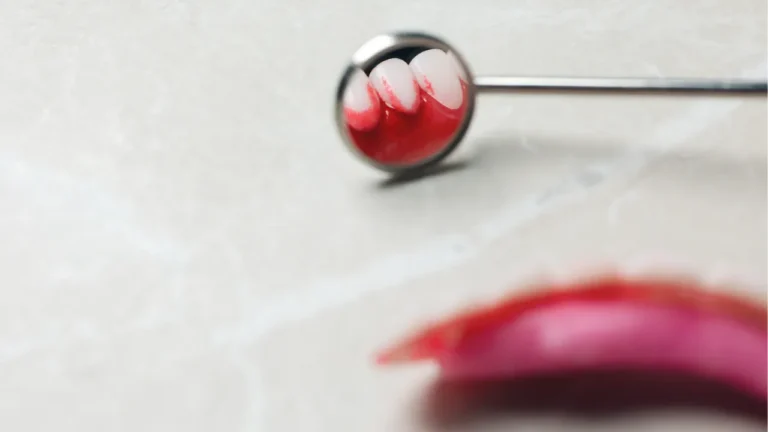
Common Symptoms of Gum Disease
In its early stages, gum disease can be subtle. Watch for these warning signs:
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Bleeding when brushing or flossing
- Persistent bad breath
- Gums pulling away from the teeth (receding gums)
- Loose or shifting teeth
- A change in the way your teeth fit together when you bite
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to see a dentist as soon as possible. The earlier gum disease is treated, the better the outcome.
Stages of Gum Disease
- Gingivitis – The earliest stage, marked by gum inflammation and bleeding. It’s reversible with professional cleanings and good oral hygiene.
- Early periodontitis – Plaque spreads below the gumline, causing tissue damage and mild bone loss.
- Moderate to advanced periodontitis – Significant bone loss, loose teeth, gum recession, and possible tooth loss.
How Is Gum Disease Treated?
Treatment depends on the severity of the condition:
1. Professional Cleaning
For gingivitis, a routine cleaning may be enough to remove plaque and tartar. You’ll also receive guidance on improving your home care routine.
2. Scaling and Root Planing
This deep-cleaning procedure removes tartar from below the gumline and smooths the root surfaces, helping the gums reattach to the teeth.
3. Medications
Antibacterial rinses, gels, or oral antibiotics may be used to control infection.
4. Surgical Treatment
In advanced cases, gum surgery or bone grafting may be necessary to repair the damage and preserve your teeth.
Preventing Gum Disease
The best way to avoid gum disease is through consistent, proactive care:
- Brush at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste
- Floss daily to remove plaque between teeth
- Visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings
- Avoid smoking or tobacco use
- Eat a balanced diet and stay hydrated
Don’t Ignore the Signs
Gum disease is progressive—but it’s also preventable and manageable when caught early.
At Every Smile Dental, we provide thorough periodontal evaluations and treatment plans tailored to your needs.
Whether you’re noticing early signs or managing long-term gum health, we’re here to help.